Bursitis
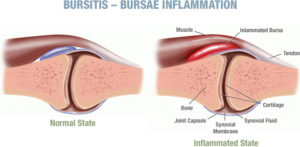
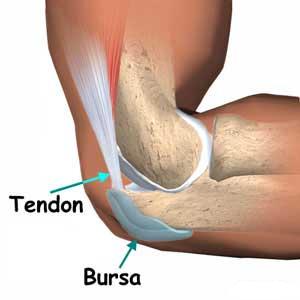
Bursitis can be very painful. It can affect your movement, comfort, even your ability to sleep. Quite simply, bursitis is the inflammation and irritation of a bursa. These structures are basically fluid filled cushions that soften impact and dampen friction between structures of the body (bones, tendons, ligaments etc).
Bursa, like tendons, are located throughout the body. The commonly known ones are associated with your larger, heavily used joints (hip, elbow, knee, shoulder, heel and ankle).
How Does Bursitis Develop?
Repetitive motions may cause excess friction, which in turn could lead to inflammation of the bursa. This is similar to how repetitive motions can cause tendonitis.
This may also occur when the bursa suffers compression for extended periods of time (eg sleeping on your side or kneeling for long periods).
Injury is another cause of bursitis, as are certain underlying autoimmune conditions, like gout or arthritis.
Age can also be a risk factor in the development of bursitis. As a person ages there tendons become less elastic, less resistant to stress, and easier to tear.
Symptoms
- Localized tenderness
- Swelling
- Pain during compression and movement.
Diagnosis
Sometimes it can be so obvious that it can be diagnosed through a good history. A thorough examination is also important. When chronic (long term), an x-ray may be able to reveal local calcium deposition.
Dr Google is not the answer!
Management
Bursitis can take months to heal properly. When chronic, the accumulation of excessive scar tissue (fibrosis) can cause the condition to become chronic and last much longer, sometimes even years. This is why prompt diagnosis and proper treatment aimed at reducing the possibility of these complications is vital in the treatment of bursitis.
In the early stages of managing bursitis it is important to decrease inflammation, ice therapy (home care), supplements/medications, along with manual therapy (chiropractic, massage, acupuncture, physiotherapy) aimed at safely breaking down scar tissue. Once a patient’s bursitis is stabilized, further manual therapy can then be very effective in loosening up the related soft tissue, restoring flexibility and alleviating pressure and friction over the affected bursa.
The post symptomatic/ rehabilitative stage of care is very important. Why? Bursitis is often a symptom of a more long term underlying condition. Posture, good joint mechanics and muscle function needs to be restored to a satisfactory level to reduce the risk of recurrence.
If you suffer from bursitis, know of someone who does, or require more information feel free give us a call on 38921440, send us an email, or contact us via our website https://www.yerongachiropractic.com.au/contact/ .
We are here to help!
Leave a reply